
There are 122 billion spam emails sent around the world every day. that’s 85% of the world’s email traffic. the scale is impressive and disturbing at the same time. nobody likes spam, especially mail services. therefore, many systems are waging war on spam. however, bona fide businesses also fall under its sanctions. How to avoid becoming a spammer by accident and send emails the right way? let’s find out.
what is spam
spam are unsolicited mass messages sent by email or other digital channels such as SMS or social networks. spammers make this type of mailing without the consent of the recipient to a large number of users. In most cases, the cards offer goods or services of dubious quality.
the origins of spam
In the 1940s, the word “spam” had no negative connotation. Spam was the brand of canned food made by the Hormel Foods Corporation. The company produced it to keep soldiers nourished during World War II. after the war, many products remained. The Hormel Corporation had to sell them before the end of their useful life. in short, as fast as possible. so after a couple of weeks, junk canned food ads were everywhere. the product was aggressively imposed on people.
When mass “junk” messages appeared on the internet, they began to be tagged with the word “spam”. At first, this method might be effective, but now the spam messages are annoying. people are used to ignoring them in the great flow of information. but the spam market is not losing momentum.
spam has penetrated almost all digital communication channels. In addition to emails, we encountered spam:
- in forums where users leave hidden advertising messages;
- in comments and private messages on social networks;
- on review sites;
- in messengers and sms.
Automation has accelerated spam delivery and increased it significantly. now a spam bot can replace a person, for example when spamming on social media platforms. although it is not too difficult to determine if you are communicating with a real person or with a machine. bots aren’t very smart, you can break their logic with an unexpected response.
types of spam
advertising spam are regular marketing emails sent to addresses on your contact list.
Fake messages are letters from ordinary people who tell their tragic story and ask for money, or promise to give a large amount like this:
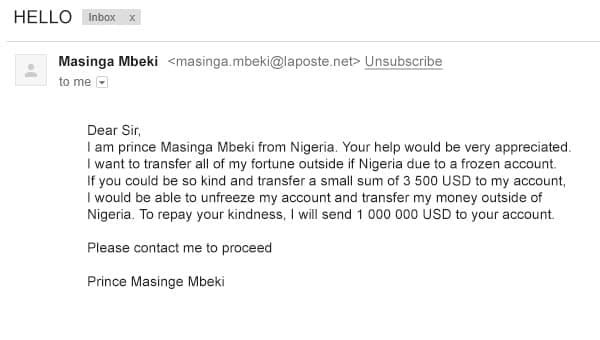 Example of a spam message from a «real person»
Example of a spam message from a «real person»
phishing emails are sent by spammers trying to trick you by posing as a well-known brand. the sender’s email contains a false email address. usually the user does not even notice it. understand that he was cheated after following the link. the objective is to obtain personal and confidential data. a link in this letter leads to a fake website where the user is asked to leave their full name, passwords, bank card numbers and other information.
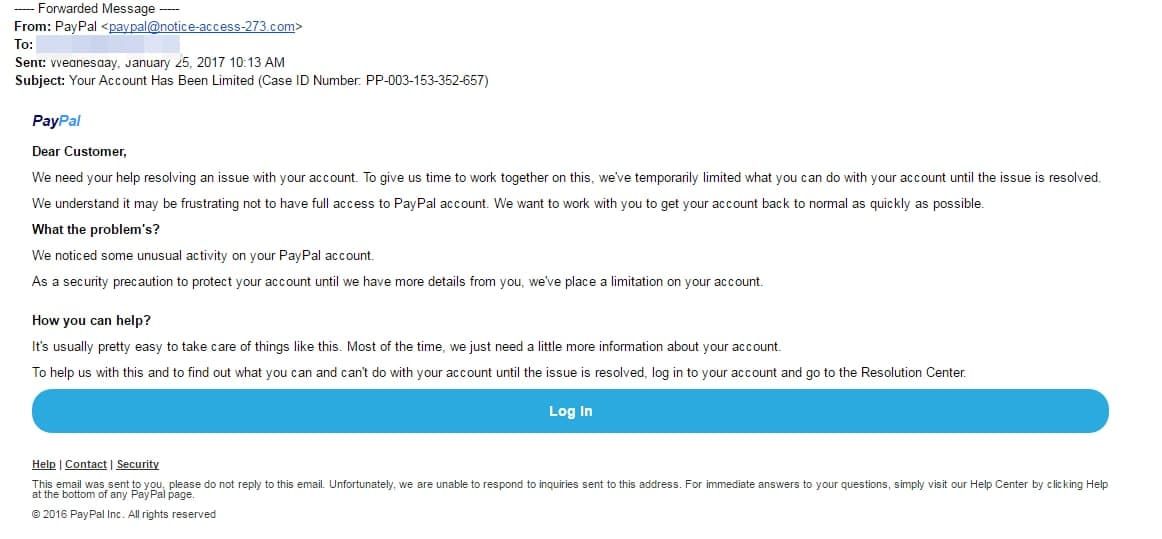 Phishing email mimicking PayPal
Phishing email mimicking PayPal
malware emails are virus letters. the user clicks the link and gets a virus on their device.
why do users get spam?
The reason for spam is data that fell into the wrong hands. how spammers get user addresses:
- data leak: the address was stolen from the contact list of the compromised account.
- analysis of email addresses from websites.
- use of an email builder that iterates over possible options some may turn out to be active.
- purchased email lists – sold by unscrupulous companies or individual employees.
who sends spam?
both professionals and random people, such as inexperienced sellers, can send spam. spammers are divided into:
- pros are mail services that send a large number of emails. such teams know your business well and may even have programmers on staff for more advanced solutions.
- email address harvesters use software to verify and sell databases.
<li Inexperienced and accidental spammers are often marketers who don’t understand what a newsletter is and do it poorly. A novice spammer does not delve into the details of sending, and that is why letters from him fall under the sanctions of services.
In order not to be among the ranks of accidental spammers, it is necessary to prepare for sending. you need to know the legal, technical and other peculiarities.
how to avoid spam filters
The spam folder is a prayer for your email. why? the client will not know about you, the consequences can be more serious: domain disconnection, lawsuits and fines.
To find out why emails end up in the spam folder, you need to evaluate many factors:
- the legality of the submission;
- domain reputation;
- technical configuration of the mailing list;
- if the rules of the providers of mail are being followed.
let’s look at each point.
the legality of the shipment
If you send commercial email, you must comply with the requirements of the can-spam law. otherwise, you will have to pay a large fine.
how not to break the law:
- do not use false or misleading header information: headers, source names, reply-to addresses, or subject lines.
- make it clear to recipients that your message is an advertisement.
- Tell recipients how to unsubscribe: Provide a link to unsubscribe.
- tell recipients where you are. Your message must include your valid physical mailing address: address, a PO Box, or private mailbox.
domain reputation
The reputation of the domain you use to send email depends on the following factors:
- whether the ip address is blacklisted or not,
- the quality of the email database,
- whether the email authentication passed or not,
- how many unread emails and spam complaints,
- how high the ctr is,
- the intensity of the emails.
database quality
“bad” addresses in the database also affect the mailing list, so you must observe email hygiene: clean up duplicate and inactive emails.
possible database problems:
The address was not validated. The user left an inactive or incorrect email.
The foundation was not used immediately.
in this case, the contacts become obsolete. this happens if a company collects an email database for a long time in different ways, but does not send messages right away. for example, because you are expecting a certain number of clients in the contact list.
database errors
The contact list may contain recipients who have unsubscribed but are still receiving emails. increases the risk of receiving spam complaints from those people. at worst, you can get sued.
spam traps in the database
spam traps are email addresses controlled by isps or blacklist operators. these addresses are used to find spammers. a spam trap can be an email address that used to belong to a real person, but the user hasn’t logged into the account for a long time. Another type of spam trap is a specially created one. If a newsletter arrives at this address without consent, the service may consider it spam. if there are too many such addresses in the database, the sender reputation gets worse.
spam complaints
People complain even when they initially consent to receive the newsletter. what could be the reasons for the complaints:
- incorrect or offensive subject;
- mail error: the user received the letter again, although he unsubscribed;
- changed the subject of the mail: “no no I subscribe to this”;
- partner offers in letters.
user behavior
Email services count how often users open emails and click on the links they contain. the fewer clicks, the more likely you are to receive spam in the future.
newsletter content
The service can block sending mail if your html document is not valid. It is forbidden to use dangerous elements, such as javascript, vbscript, frames, activex iframes, java applets, css connected to external websites, metarefresh, etc. In addition, services do not accept links that have been shortened with special tools.
intensity and volume of shipment
services love predictable behavior. a sudden spike in email volume or sending irregular email patterns are signs of spam.
blacklists
An email blacklist is a list of IP addresses or domains that have been flagged as suspicious for sending spam emails. there are private and public blacklists. private blacklists are created by users when they restrict the receipt of letters from a specific sender. it’s not too dangerous. however, if a domain or IP address is on a public blacklist, letters can be blocked from a large subset of addresses on this blacklist.
ip address and domain can be blacklisted for:
- sending newsletters to irrelevant addresses;
- a lot of spam traps in the email database;
- sending emails without recipient confirmation .
so it is important to check if you are blacklisted. for example, mxtools will tell you where you have been blacklisted.
how to maintain your reputation
- use the double option and continue sending only when the user has confirmed their email.
- monitor ip address and domain ratings on special services regularly.
- clean up the database, delete inactive contacts and check for errors.
- warm up ip addresses – Gradually increase mail volumes.
- monitor the quality of your content and try different engagement techniques if your emails stop being opened. but know when to stop and don’t try dubious techniques, eg clickbait.
technical configuration and architecture of email messages
all mail services support the same standards for spam protection. there are technical headers on the servers from which the newsletter is sent. this is where the data about the message is placed. this data determines the reliability of the sending source.
which parameters should be in the “correct” letter:
rfc (request for comments) is a document that contains technical specifications and standards.
dns (reverse dns lookup and ptr records) – All servers you use to send email must have valid dns records. no automatically generated reverse dns lookup and ptr records. if reverse dns is not specified, the mail service will not pass such mail.
ip addresses (whois). never hide ip address data in whois. it is especially important when the hoster has been hacked and spam is being sent from their ip. if there is no data about you, the service cannot tell you about the problem and will simply block all mail.
proxy and relay are spam protection on your behalf. the server does not have to be with an open proxy server or an open relay. in this case, anonymous and unauthorized users will not be able to access it.
dkim (Domain Key Identified Mail) is a digital signature protocol that determines if the sender is eligible for delivery. the email provider identifies it through a special key.
spf (sender policy framework) is a record that will show which domains and ip’s the email will come from. this setting must be in all dns, otherwise the mail service will send a spam letter or warn of a threat.
fbl (comment search) is a standard that displays information about spam complaints. each email sender can use fbl to find out which user has complained about which email.
list-unsubscribe is setting the unsubscribe address or url. the user can unsubscribe without clicking through an unsubscribe link.
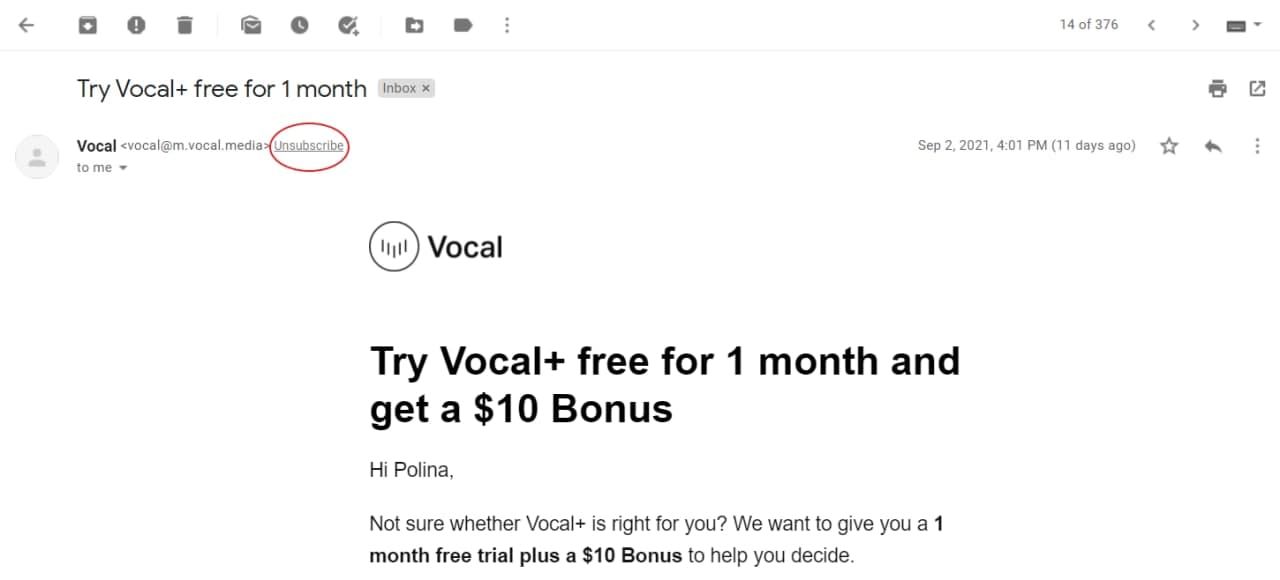 List-unsubscribe option in Gmail
List-unsubscribe option in Gmail
The
dmarc policy is a standard that helps domain owners establish rules for their mail services. using them, the postal provider will know what to do with letters that were sent from the owner’s domain, but did not pass email authentication. this will protect against dkim forgery and the use of services where any fraud can put any domain. dmarc also helps control technical settings.
administrative requirements for mailbox providers
If you want the message to bypass spam filters, the requirements of the mailbox providers must be followed. Otherwise, you may fall under sanctions such as:
- email volume limitation;
- block sending;
- mark as spam.
let’s take a closer look at the requirements for gmail.
- set up reverse dns lookup for ip addresses.
- separate form addresses by content type. use the first to send promotions, the second to send receipts, and the third for notifications.
- don’t send phishing emails from your domain.
- don’t send letters on behalf of another domain if you do not have the right to do so.
- authenticate messages.
- send mail only to interested users who have consented to receive the newsletter. the service also offers to periodically renew subscription consent.
- make it easy to unsubscribe.
- send emails at a specific time and start sending small batches. the more letters there are, the slower it will be to increase their number.
- monitor the reputation of ip addresses: if they are blacklisted.
important! Always check the requirements of mailbox providers before sending emails. even a small violation of the rules can result in a spam folder.
altcraft platform for successful submissions
Our platform helps automate marketing processes and build business. marketers use it to send emails without additional services. the altcraft platform allows:
- optimize delivery to inbox folder;
- avoid blocking;
- speed up delivery of some categories of letters;
- reduce shipping costs.
the technologies we work with:
spf (sender policy framework) is a domain authentication technology.
dkim (domain key identified mail) is a digital signature that the recipient’s mail server automatically verifies and clears its reputation.
dmarc will tell the mail service what to do if something is wrong with the spf records.
bimi (mark indicators for message identification) works with dkim, spf and dmarc. helps to identify companies by the image of the brand next to the subject of the letter. this is an additional validation of the sender.
fbl (feedback loop) is a standard that returns spam complaints to the sender of emails.
With the altcraft platform, there is no need to worry about emails turning into spam. just create your own newsletter or use a ready made email template.
 Email templates in Altcraft Platform
Email templates in Altcraft Platform
conclusion
The path of email newsletters is thorny and challenging. one day, emails from any company can end up in the spam folder. but don’t give up on this channel just because of the complexity. competent approach and good service will help to send emails correctly and increase sales.
